Thai Tones – Simple Guide
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Tone Marks in Thai (วรรณยุกต์)
Thai uses 4 tone marks. They combine with consonant classes to produce tones.
| Tone | Thai Name | Phonetic Tone Mark | Thai Symbol | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mid | สามัญ (mid) | none | none | กา |
| low | ไม้เอก (low) | ̀ | ่ | ก่า |
| falling | ไม้โท (falling) | ̂ | ้ | ก้า |
| high | ไม้ตรี (high) | ́ | ๊ | ก๊า |
| rising | ไม้จัตวา (rising) | ̌ | ๋ | ก๋า |
Important:
Tone = consonant class + vowel length + tone mark.
Tone marks alone are not enough to guess the correct tone.
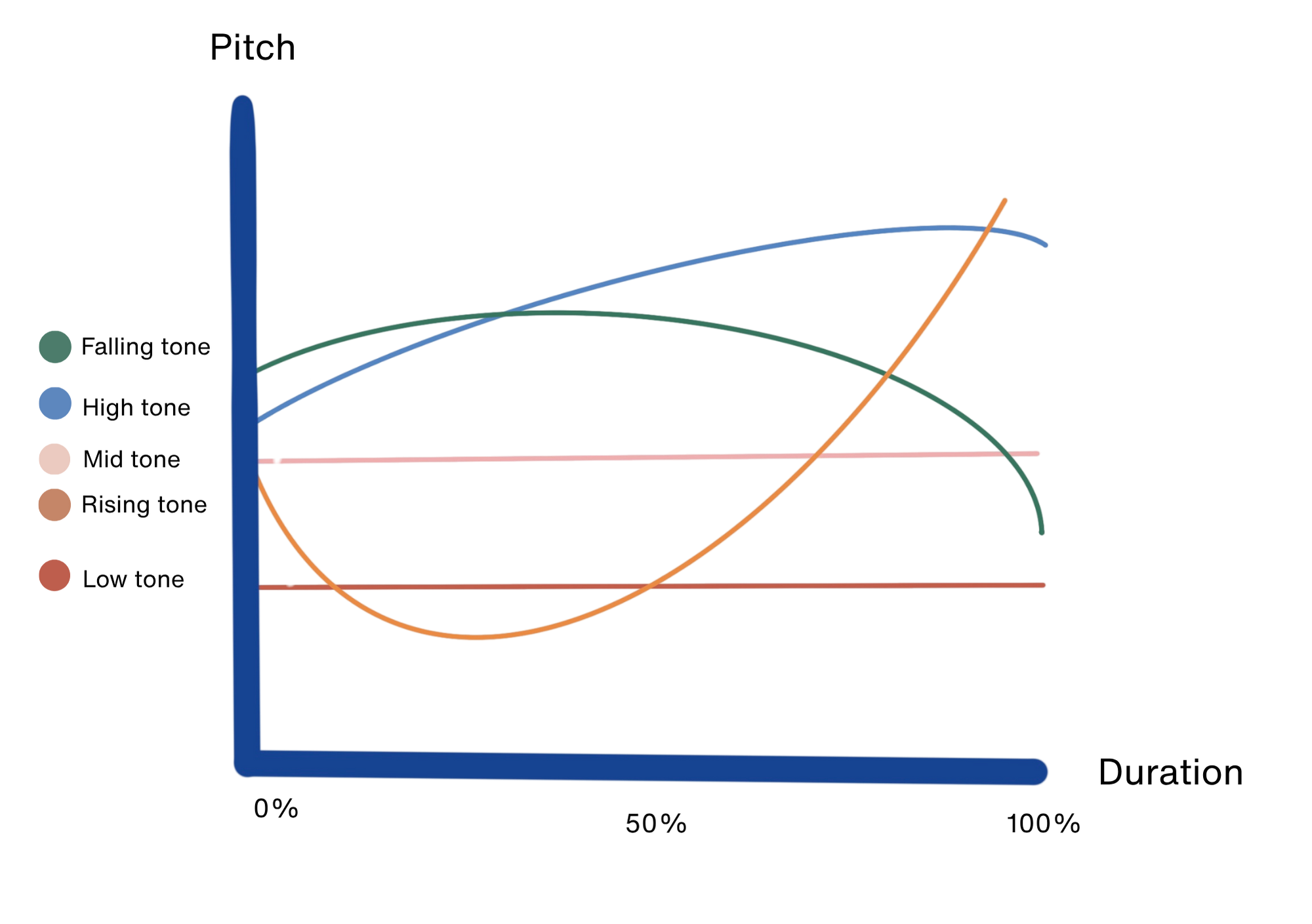
1. Mid Tone (เสียงสามัญ)
Tone: flat, steady
Example word: กา – gaa (crow)
Example sentence:
ไปไทยกัน /pay thai gan/ – Let’s go to Thailand.
2. Low Tone (เสียงเอก)
Tone: low and calm
Example word: ก่า – gàa
Example sentence:
ตอกไข่ไก่ /tɔ̀ɔk khày gày/ – Crack chicken eggs.
3. Falling Tone (เสียงโท)
Tone: starts mid, drops quickly
Example word: ก้า – gâa
Example sentence:
บ้านไม่ใกล้ /bâan mây glây/ – Home isn’t close.
4. High Tone (เสียงตรี)
Tone: starts mid, rises high
Example word: ก๊า – gáa
Example sentence:
ซื้อน้ำมั้ย /sʉ́ʉ náam máy/ – Wanna buy water?
5. Rising Tone (เสียงจัตวา)
Tone: starts low, rises like a question
Example word: ก๋า – ǵaa
Example sentence:
หมาสีขาว /mǎa sǐi khǎaw/ – The dog is white.
| Tone | Mid | Low | Falling | High | Rising |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thai | มา | หม่า | ม่า | ม้า | หมา |
| Phonetic | maa | màa | mâa | máa | mǎa |
| Audio |
| Tone | Mid | Low | Falling | High | Rising |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thai | ลา | หล่า | ล่า | ล้า | หลา |
| Phonetic | laa | làa | lâa | láa | lǎa |
| Audio |
| Tone | Mid | Low | Falling | High | Rising |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thai | ไก | ไก่ | ไก้ | ไก๊ | ไก๋ |
| Phonetic | gay | gày | gây | gáy | găy |
| Audio |
